What are Hives?
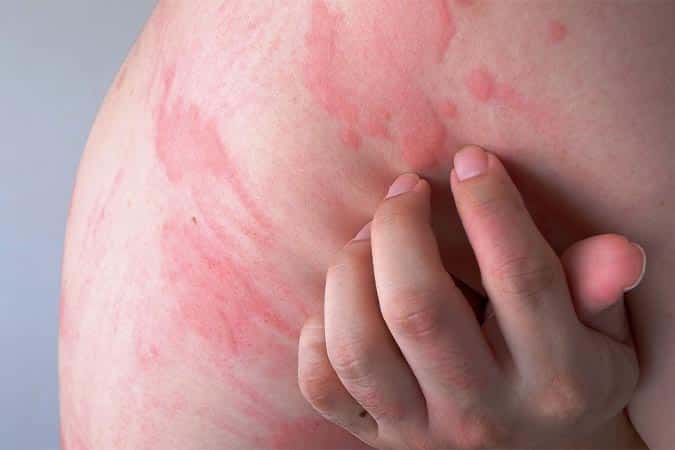
Hives are swollen pink rashes that appear suddenly, as a result of certain allergens or for unknown reasons. These bumps usually itch, but may also burn or sting. Hives can pop up anywhere on the body, including the face, ears, lips, tongue, and throat. When you press on the center of the hives, it may turn white, which is called “blanching”.
There are a variety of things that may trigger the onset of hives including certain foods, medications, insect bites or stings, latex, cold, heat, or exercise, pollen, pet dander, some plants, viral infections, bacterial infections, and more.
Who is a Good Candidate for Hives Treatment?
Individuals who have severe hives or hives that do not go away after several days should see a dermatologist for assessment. If you experience hives along with dizziness, difficulty breathing, tightness in the chest, or swelling of the tongue, lips, or face, call 9-1-1 and contact a doctor immediately, as these may be signs of a serious allergic reaction.
What to Expect During Hives Treatment?
In order to correctly diagnose your hives, your dermatologist may ask many questions to find the cause. Skin tests may be done to determine if you are allergic to anything that is causing hives. Routine blood tests may also be performed. The best treatment is to identify and remove the trigger that causes hives. In the meantime, there are a number of treatments that be used, including:
Antihistamines: These pills help to block the release of histamine, which causes symptoms.
Heartburn/GERD medications: Also known as H-2 receptor antagonists, these medications are taken orally to supplement the effects of H1 blockers.
Anti-inflammatory medications: Oral corticosteroids like prednisone can help to lessen redness, itching, and swelling. These medications are only used for a short time to control hives, as they can lead to side effects over time.
Immune-suppressing drugs: For cases of severe or chronic hives, these drugs may be recommended.
Biologic drug: Omalizumab (Xolair) has been approved to treat chronic hives in those 12 years of age and older.
For mild hives, there are some at-home treatments that can help to reduce symptoms, including applying cool compresses on the affected areas, wearing loose-fitting and light clothing, and trying to sleep and work in a cool room.
Hives FAQs
Can a blood test detect hives?
Can a dermatologist help with hives?
Can alcohol cause hives?
Can anxiety cause hives?
Can high blood pressure cause hives?
Can hives be mistaken for eczema?
Can hives get infected?
Can hives look like bug bites?
Can hives not be itchy?
Does Benadryl help hives?
Following Hives Treatment
Following treatment for hives, patients experience an improvement in their symptoms, as well as the disappearance of their hives over time. Your dermatologist will inform you if there are any steps that need to be taken following treatment.
In order to avoid hives in the future, it is best to avoid or eliminate the trigger. This may include avoiding certain foods, harsh soaps or lotions, harsh sunlight, certain medications, or tight clothing.
Schedule a Consultation
If you are bothered by hives and are looking for a solution, contact HMGS Dermatology today! We will help you to schedule a consultation with one of our dermatology specialists to get you started on your journey to feeling healthy and happy!
Get Started With A Visit!
Fill out the form below and we will reach out to you shortly to schedule an appointment.